Favorable variable overhead efficiency variance indicates that fewer manufacturing hours were expended during the period than the standard hours required for the level of actual output. Variable overhead efficiency variance is favorable when the standard hours budgeted are more than the actual hours worked. This means that the company’s workforce spends less time than budgeted to complete the production. In other words, the company is more efficient than expected in completing the task. An adverse variable overhead efficiency variance suggests that more manufacturing hours were expended during the period than the standard hours required for the level of actual production.
Standard Cost for Actual Output (Variable Overhead)
However, due to labor inefficiency, it took them 5,000 hours to meet the required production. When the actual hours worked are less than the budgeted hours estimated by management, we called this difference a favorable variance. Using the information given below, compute the fixed overhead cost, expenditure, and volume variances. This shows the over/under absorption of fixed overheads during a particular period.

How to Compute Various Overhead Cost Variances
Such an estimate is then incorporated into the total variable overhead expense. Thetotal standard cost for diesel oil is then calculated by multiplying thequantity with the standard rate at which diesel oil will be bought. Controlling overhead costs is more difficult and complex than controlling direct materials and direct labor costs. This is because the responsibility for overhead costs is difficult to pin down.
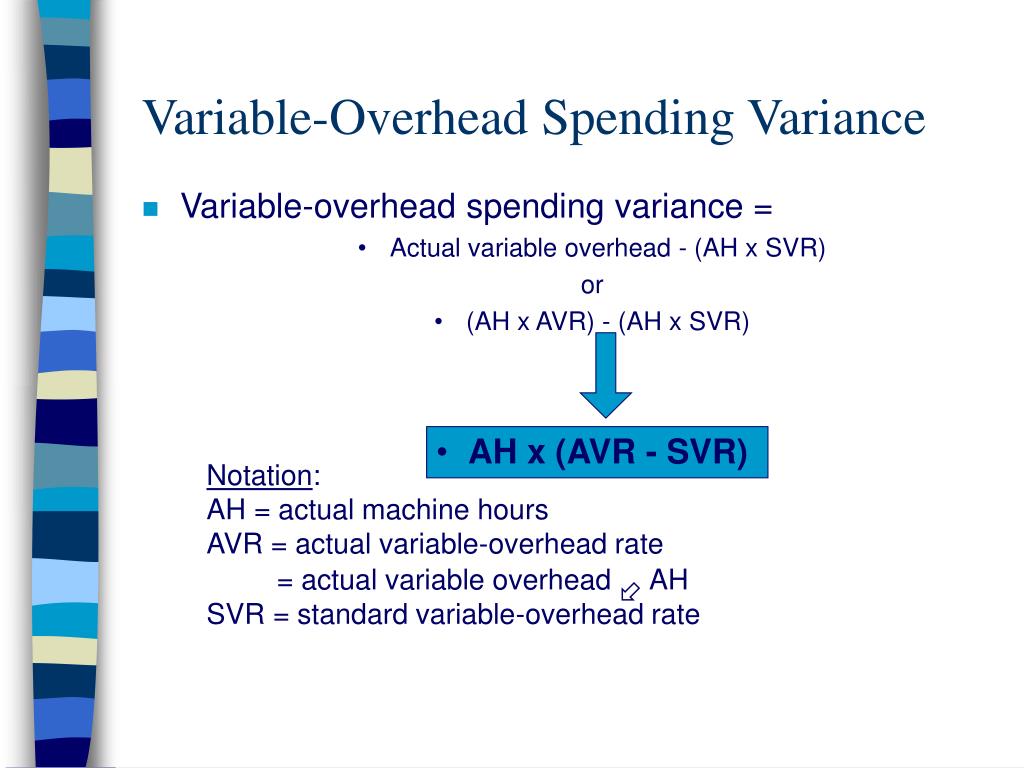
Formulae using Inter-relationships among Variances
This is a portion of volume variance that arises due to high or low working capacity. It is influenced by idle time, machine breakdown, power failure, strikes or lockouts, or shortages of materials and labor. This example provides an opportunity to practice calculating the overhead variances that have been analyzed up to this point.
The variable overhead efficiency variance is the difference between the actual and budgeted hours worked, which are then applied to the standard variable overhead rate per hour. A favorable variance means that the actual hours worked were less than the budgeted hours, resulting in the application of the standard overhead rate across fewer hours, resulting internal revenue in less expense being incurred. However, a favorable variance does not necessarily mean that a company has incurred less actual overhead, it simply means that there was an improvement in the allocation base that was used to apply overhead. For example, the company ABC, which is a manufacturing company spends 480 direct labor hours during September.
- This means that the company spends more time than the budgeted standard time to complete the work.
- Tocalculate the standard rate of variable overhead per hour the budgeted totalvariable overhead expense is divided by the budgeted hours necessary forproduction.
- This is a portion of volume variance that arises due to high or low working capacity.
- By contrast, efficiency variance measures efficiency in the use of the factory (e.g., machine hours employed in costing overheads to the products).
Practice Question
If the variance is significant, the company must take appropriate measures to reduce such overheads to a minimum. The standard rate is adjusted per all price-increasing/decreasing factors (inflation rate, different suppliers, etc). For example, the quantity of diesel oil utilized is estimated based on previous production units.
Thus, the production department does the same and provides an estimate of production costs that will be incurred in the following year. Our writing and editorial staff are a team of experts holding advanced financial designations and have written for most major financial media publications. Our work has been directly cited by organizations including Entrepreneur, Business Insider, Investopedia, Forbes, CNBC, and many others. This team of experts helps Finance Strategists maintain the highest level of accuracy and professionalism possible.
To enable understanding we have worked out the illustration under the three possible scenarios of overhead being absorbed on output, input and period basis. Since the formula for this variance does not involve absorbed overhead, the basis of absorption of overhead is not a factor that influences the calculation of this variance. And that’s why the efficiency graph goes higherand in the end, the result is a favorable one. Variable overhead is an indirect production expense that varies based on production.
An unfavorable variable overheadefficiency variance is when the standard hours required for production are lessthan the actual hours worked. So, the company ABC has a $400 favorable variable overhead efficiency variance in September. This is due to the company ABC spends only 480 hours which is 20 hours less than the standard hours that are budgeted. Standard variable overhead rate is the rate that can be determined with the budgeted variable overhead cost dividing by the level of activity which in this case is either labor hours or machine hours. Variable Overhead Efficiency Variance is the measure of impact on the standard variable overheads due to the difference between standard number of manufacturing hours and the actual hours worked during the period. On the other hand when actual hours exceed standard hours allowed, the variance is negative and unfavorable implying that production process was inefficient.
Variable overhead efficiency variance is one of the two components of total variable overhead variance, the other being variable overhead spending variance. This is a cost that is not directly related to output; it is a general time-related cost. Specifically, fixed overhead variance is defined as the difference between Standard Cost and fixed overhead allowed for the actual output achieved and the actual fixed overhead cost incurred. Variable Overhead Efficiency Variance is traditionally calculated on the assumption that the overheads could be expected to vary in proportion to the number of manufacturing hours. Using Activity based costing in the calculation of variable overhead variances might therefore provide more relevant information for management control purposes.
The standard direct labor hours allowed (SH) in the above formula is calculated by multiplying standard direct labor hours per unit and actual units produced. The results that arise from variable overhead efficiency variance is can be termed as a favorable or unfavorable variance. The factory worked for 26 days putting in 860 hours work every day and achieved an output of 2,050 units.
